How to Import and Sync Data Across Multiple Google Sheets
by Matas Valinčius, Founder & Lead Project Manager
No, copying and pasting it every time it changes won't cut it and you know it. That's why in this blog post, we will show you how to import and keep data in sync across multiple Google Sheets documents.
Setup
First, let's create a new Google Sheets document and name it Master. This document will contain the data that we want to sync across other documents.
Let's populate it with some random data:
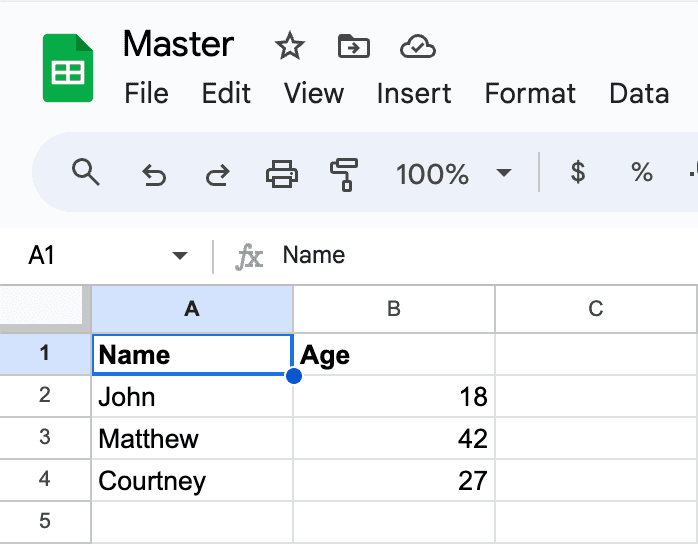
Next, create another Google Sheets document and name it Example. This document will contain the data that we want to import from the Master document.
Import Data
Google has a splendid built-in solution to our problem - the IMPORTRANGE function. This function allows you to import data from another Google Sheets document and constantly keep it in sync.
To import data from the Master document to the Example document, use the following formula:
=IMPORTRANGE("INSERT_YOUR_MASTER_SHEET_URL", "Sheet1!A:B")The first argument is the URL of the Master document. While the second argument is the range of cells you want to import. In this case, we are importing columns A and B from the Sheet1.
Once you typed in the formula in the Example document, you will see a prompt to grant access to the Master document. Click on the Allow access button to proceed.
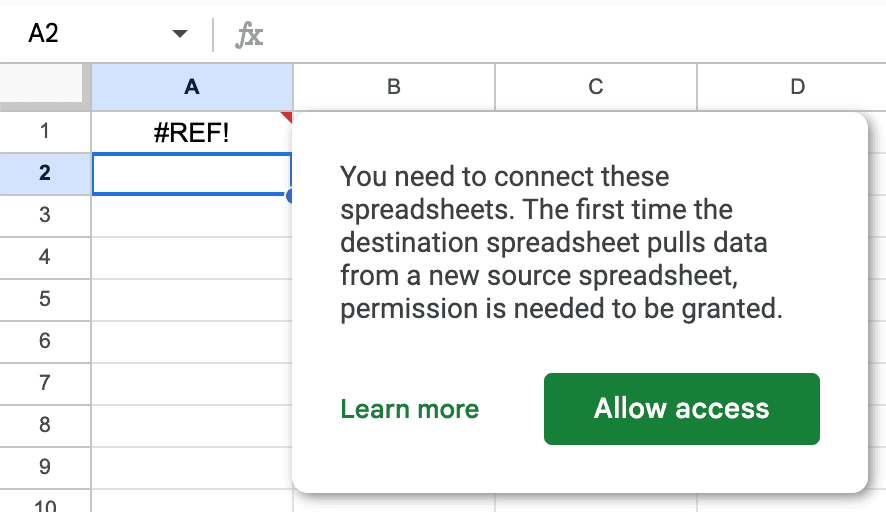
If the data is huge, it might take a while to import it. Throughout the process, you will see a loading spinner in the cell where you typed in the formula.
Once the loading is done, you should see the data from the Master document in the Example document.
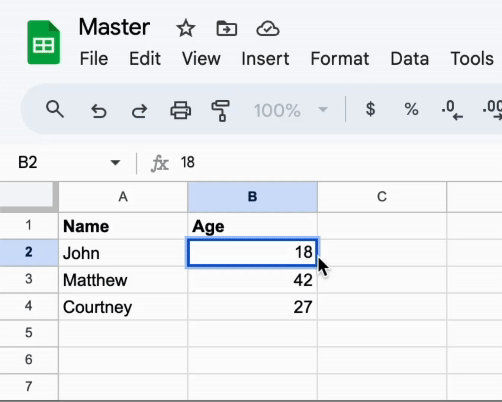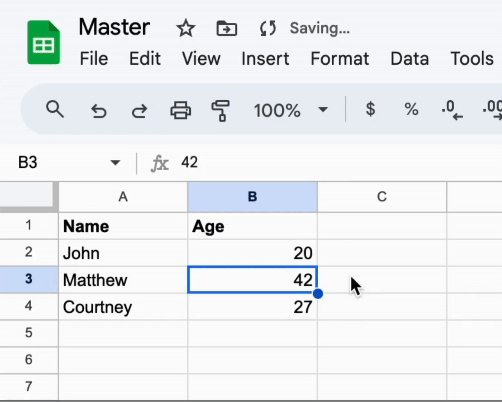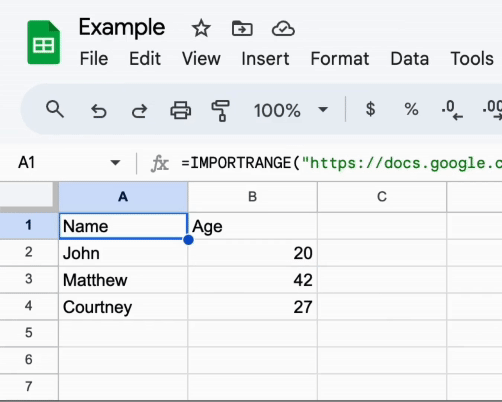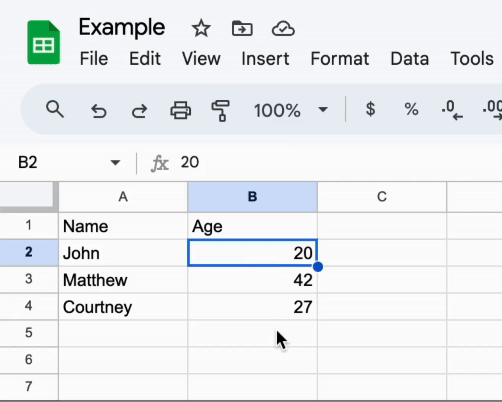
The magical part is that the data in the Example document will be updated in real-time whenever the data in the Master document changes.
Take a look:
Using Query to Filter Data
We got the data imported and synced - phenomenal. But what if you need to import only specific columns or rows from the original data?
I'm sure there are many ways of doing this but my personal favorite is using the QUERY function.
Say you want to import only the Name column (A) from the Master document. You can use the following formula:
=QUERY(IMPORTRANGE("INSERT_YOUR_MASTER_SHEET_URL", "Sheet1!A:B"), "SELECT Col1")You could obviously just change the Sheet1!A:B part to Sheet1!A:A to import only the Name column.
However, if you have a larger data table with many columns, you might want to select a few that are not next to each other. That is when you should use the QUERY function.
Okay, so filtering columns is cool, but what if you want to filter rows based on a specific condition?
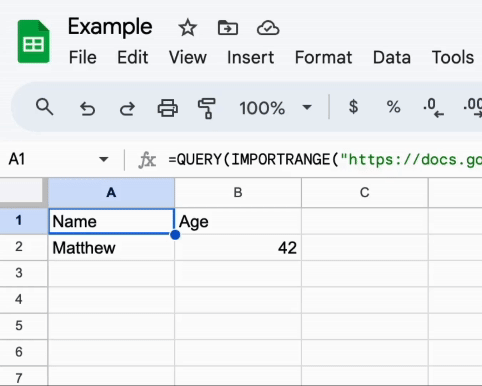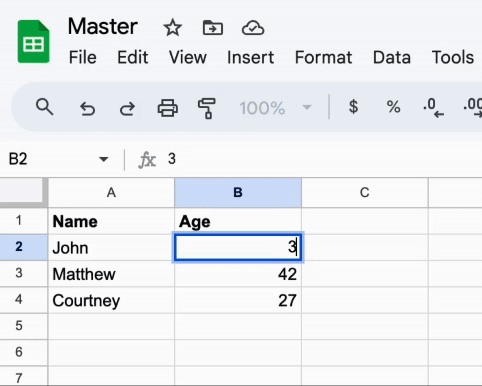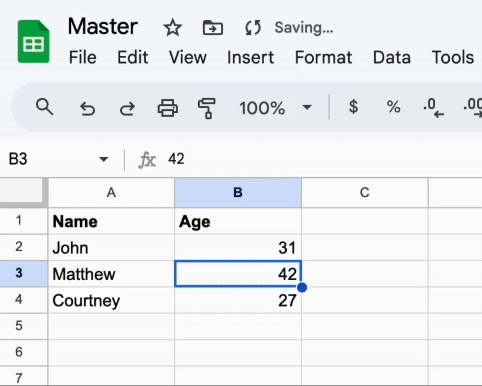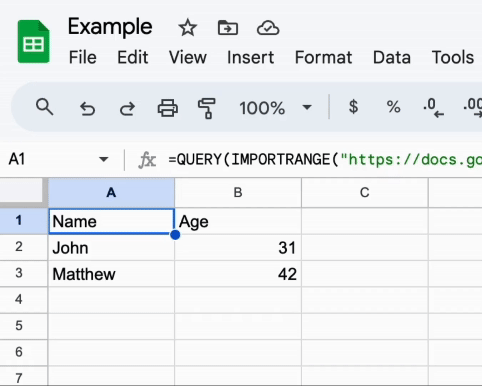
Let's say you want to import only the rows where the Age is greater than 30. You can use the following formula:
=QUERY(IMPORTRANGE("INSERT_YOUR_MASTER_SHEET_URL", "Sheet1!A:B"), "SELECT * WHERE Col2 > 30")This formula will import only the rows where Age is greater than 30.
It also dynamically adapts to changes in the Master document. Take a look:
Conclusion
IMPORTRANGE and QUERY functions are powerful tools that can help you manage data across multiple Google Sheets documents.
After reading this article, hopefully, syncing and querying data across multiple Google Sheets documents doesn't seem daunting anymore.
You can always read more about these functions in the official Google Sheets documentation.
Also, you can check out the Example document to see the formulas in action.

